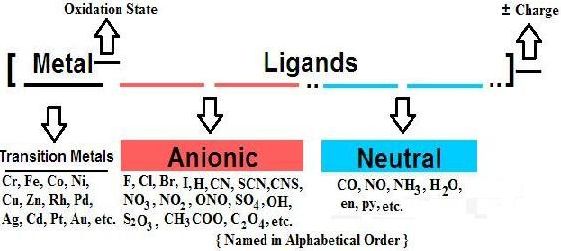
1. [FeF6]4 – is paramagnetic because
a) F – is a weaker ligand b) F – is a stronger ligand
c) F – is a flexidentate ligand d) F – is a chelating ligand.
2. An example of a bidentate (chelating) ligand is
a) NO2– b) NO3- c) en d) SO4–2 /
a) Cl- b) en c) NO2– d) I-
3. An example of a chelating ligand is
a) Chloro b) Bromo c) en d) NO2– / nitro.
4. An example of ambidentate ligand is
a) Cl– b) NO2– c) H2O d) NH3.
5. In [Fe(CN)6]4 – / [FeII(CN)6]4 – the central metal ion is
a) Fe b) Fe2+ c) Fe3+ d) (CN) –
6. The co-ordination number of Cr (III) in [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]Cl . 2H2O is
a) 3 b) 4 c) 6 d) 2.
7. The coordination number of Ni (II) in [Ni(CN)4]2 – is
a) 2 b) 4 c) 5 d) 6.
8. The coordination number of Nickel in the complex ion [NiCl4]2 – is
a) + 1 b) +4 c) +2 d) +6.
9. The geometry of [Fe(CN)6]4 – is
a) Tetrahedral b) Square Planar c) Octahedral d) Triangular
10. The geometry of [Ni(CN)4]2 – is
a) Tetrahedral b) Square Planar c) Triangular d) Octahedral
11. The type of isomerism found in the complexes [Pt(NH3)4][CuCl4] & [PtCl4][Cu(NH3)4] is
a) ionization isomerism b) co-ordination isomerism
c) linkage isomerism d) ligand isomerism.
12. Which of the following is cationic complex?
a) K4[Fe(CN)6] b) [Cu(NH3)4]2+
c) K3[Cr(C2O4)3] / [Cr(C2O4)3]3 – d) K3[Fe(CN)6].
13.The
type of isomerism found in the complexes [Co(NO2)(NH3)5]SO4 and [Co(SO4)(NH3)5] NO2
a) Hydrate isomerism b) Coordination isomerism c) Linkage isomerism d) Ionisation isomerism
FIVE MARKS
a) Hydrate isomerism b) Coordination isomerism c) Linkage isomerism d) Ionisation isomerism
FIVE MARKS
No comments:
Post a Comment